La inspección y las pruebas de PCB son pasos esenciales para garantizar que una placa de circuito impreso cumple los requisitos de calidad y funcionalidad.
Mientras que la inspección se centra en detección de defectoslas pruebas verifican integridad eléctrica y rendimiento.
Juntos, forman la puerta de calidad final antes del montaje o envío de la placa de circuito impreso.
Esta página central ofrece una visión general de los métodos de inspección y ensayo de PCB más importantes y enlaces a artículos técnicos detallados sobre cada uno de ellos.
Base de calidad:
Calidad y fiabilidad de las placas de circuito impreso
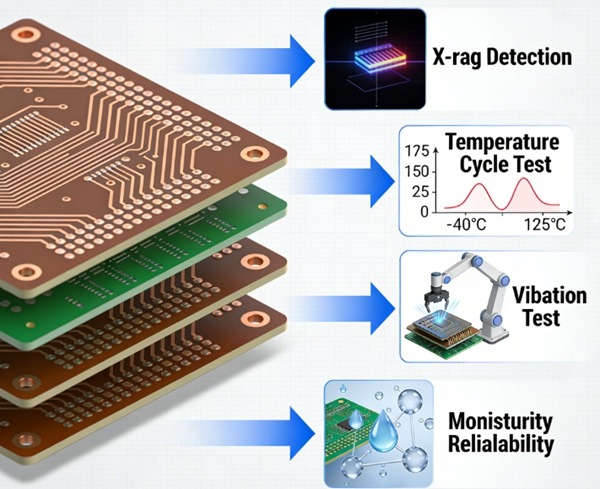
Tabla de contenidos
Por qué son importantes la inspección y las pruebas de PCB
Incluso con procesos de fabricación sólidos, pueden producirse defectos.
La inspección y las pruebas ayudan a:
- Detección precoz de errores de fabricación
- Evitar que las placas defectuosas lleguen al montaje
- Proporcionar información para mejorar los procesos
- Reducir la fiabilidad y el riesgo de fallos sobre el terreno
No sustituyen a un buen diseño ni al control de los procesos, pero reducen considerablemente los riesgos.
Inspección óptica automatizada (AOI)
La AOI es el método de inspección más utilizado en la fabricación de placas de circuito impreso.
Qué hace bien AOI
- Detecta defectos superficiales
- Identifica visualmente aperturas y cortocircuitos
- Mejora la velocidad y la coherencia de la inspección
Limitaciones de la AOI
- No puede detectar defectos internos
- No se puede verificar el rendimiento eléctrico
Inmersión profunda:
Inspección AOI en la fabricación de placas de circuito impreso
Inspección por rayos X
La inspección por rayos X permite ver las estructuras internas de una placa de circuito impreso.
Qué detectan los rayos X
- Huecos en vías y orificios
- Desalineación de la capa interna
- Delaminación y vacíos de resina
Limitaciones de los rayos X
- Mayor coste
- Velocidad de inspección más lenta
- Normalmente basado en el muestreo
Detalles técnicos:
Inspección por rayos X en la fabricación de placas de circuito impreso
Pruebas eléctricas de PCB
Las pruebas eléctricas son el único método que verifica directamente la conectividad.
Lo que confirman las pruebas eléctricas
- Continuidad de todas las redes
- Ausencia de pantalones cortos
- Conexiones de red correctas
Lo que no puede hacer
- Predecir la fiabilidad a largo plazo
- Detección de huecos internos o del grosor del chapado
Resumen del método:
Explicación de los ensayos eléctricos de PCB
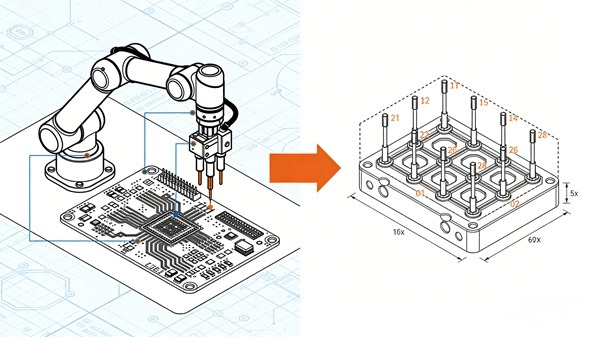
Pruebas con sonda volante frente a pruebas basadas en utillaje
Cuando es necesario realizar pruebas eléctricas, la elección del método adecuado se convierte en un factor crítico.
Factores decisivos
- Volumen de producción
- Estabilidad del diseño
- Estructura de costes
- Plazo de comercialización
Guía comparativa:
Pruebas eléctricas con sonda volante frente a fijación
Inspección frente a ensayo: entienda la diferencia
| Aspecto | Inspección | prueba |
|---|---|---|
| enfoque | Visual y estructural | Función eléctrica |
| Métodos habituales | AOI, rayos X | E-Test |
| Detecta aperturas/cortes | Limitado | Sí |
| Detecta defectos internos | Sólo rayos X | No |
| Predicción de fiabilidad | No | No |
Ambas son necesarias, pero abordan riesgos diferentes.
Cómo colaboran la inspección y las pruebas
Un sistema completo de calidad de PCB suele seguir esta secuencia:
- AOI para la detección precoz de defectos superficiales
- Inspección por rayos X de las estructuras internas (cuando sea necesario)
- Pruebas eléctricas para verificar la conectividad
- Pruebas de fiabilidad del rendimiento a largo plazo (selectivas)
Enlace de fiabilidad:
Explicación de las pruebas de fiabilidad de PCB
Aspectos económicos de la inspección y los ensayos
La inspección y las pruebas añaden costes, pero saltárselas aumenta el riesgo.
En el coste influyen:
- Complejidad del consejo
- volumen
- Profundidad de inspección
- Selección del método de ensayo
Balance de costes:
Fabricación de placas de circuito impreso: costes y calidad
Cuándo es necesaria una inspección reforzada
La inspección y las pruebas mejoradas son especialmente importantes para:
- Placas de circuito impreso de alta densidad o multicapa
- Nuevos diseños o materiales
- Aplicaciones de alta tensión o alta temperatura
- Productos de larga vida útil
En tales casos, la inspección estándar por sí sola es insuficiente.
En tales casos, la inspección estándar por sí sola es insuficiente.

Cómo aplican los fabricantes la inspección en la práctica
En entornos de producción reales, las estrategias de inspección se adaptan a:
- Riesgo de diseño
- Economía de volumen
- Requisitos del cliente
En TOPFAST, los métodos de inspección y ensayo se seleccionan en función de nivel de riesgo y necesidades de la aplicacióngarantizando eficiencia y fiabilidad.
Conclusión
La inspección y las pruebas de PCB son salvaguardias esenciales que tienden un puente entre los procesos de fabricación y el rendimiento en el mundo real.
Mediante la combinación de AOI, inspección por rayos X, pruebas eléctricas y estrategias de prueba adecuadas, los fabricantes pueden reducir significativamente el riesgo de defectos y mejorar la calidad general de las placas de circuito impreso.
Esta página central sirve como referencia central para los Inspección y pruebas de PCB grupo temático.
Preguntas frecuentes sobre inspección y pruebas de PCB
R: No. La inspección no puede verificar la conectividad eléctrica.
R: No. Detectan distintos tipos de defectos.
R: No. Los rayos X suelen utilizarse para diseños complejos.
R: No. Las pruebas de fiabilidad son necesarias para la validación a largo plazo.
R: Sólo para aplicaciones de bajo riesgo y complejidad.